Over 3,000 strokes prevented and 800 lives saved through national drive to detect and treat irregular heart rhythm
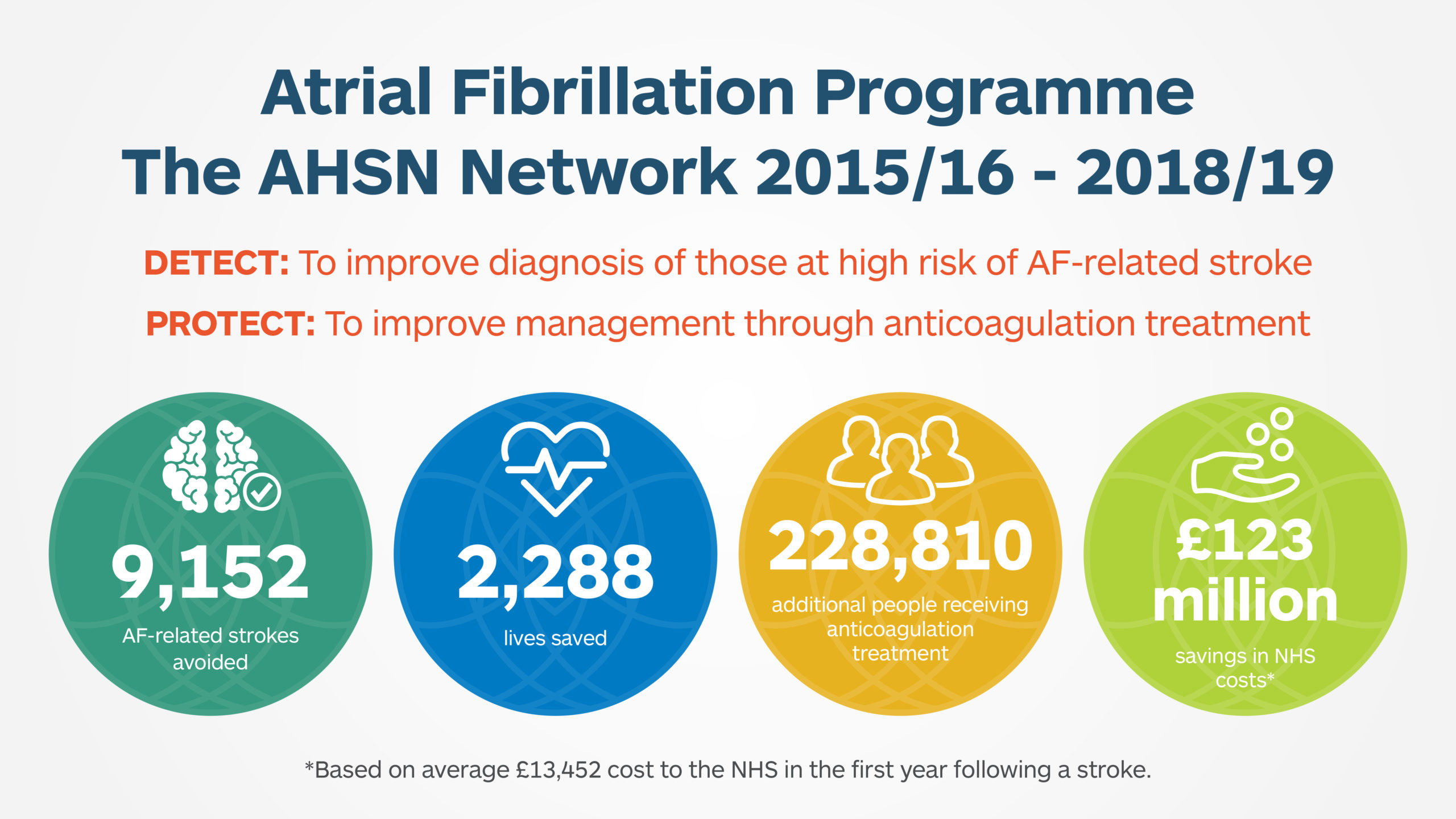
Recently released figures reveal that a programme rolled out across the NHS to reduce strokes related to an irregular heart rhythm prevented 3,165 strokes and 791 lives last year (2018/19).
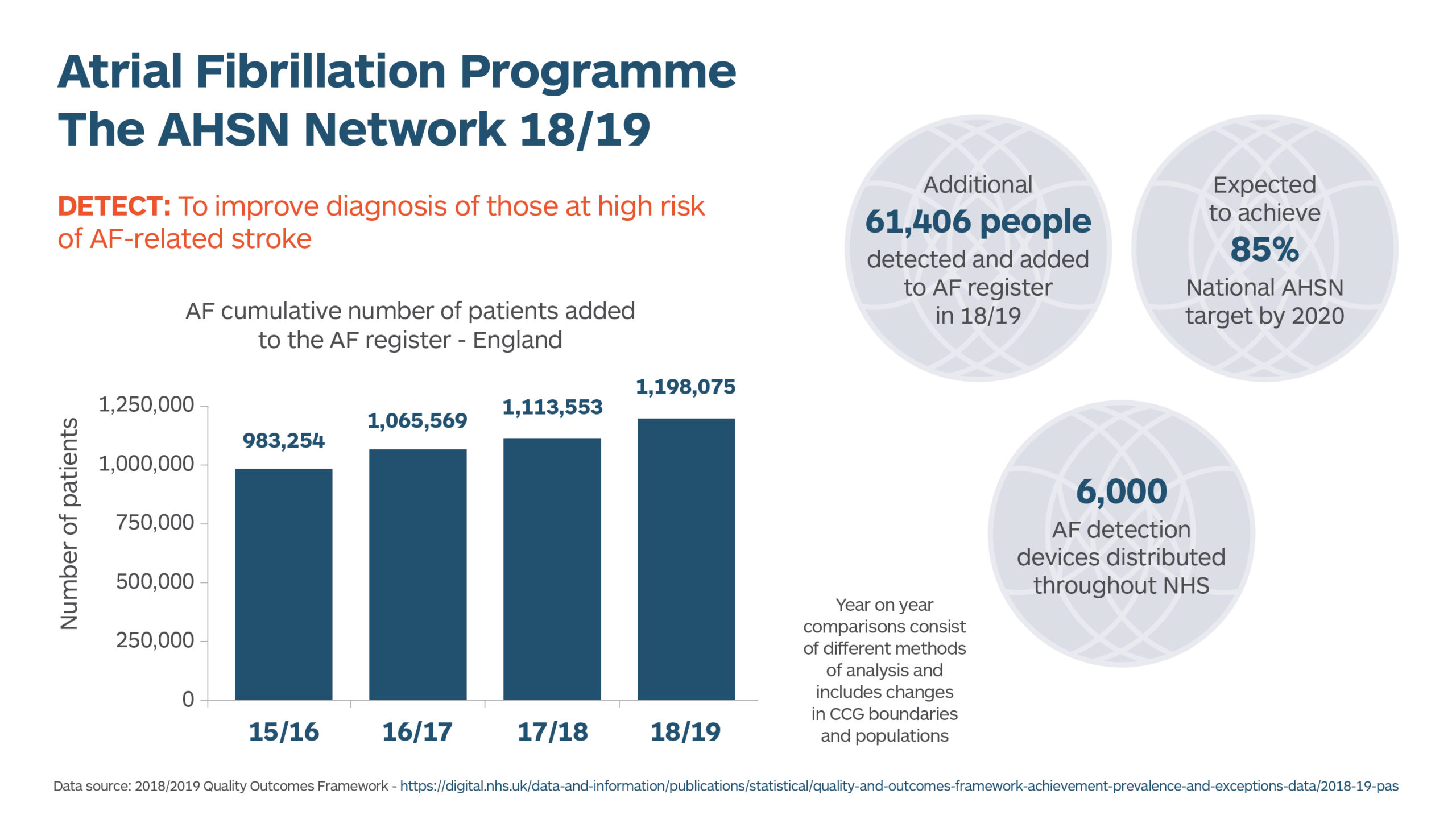
The NHS initiative focussed on improving the detection and treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) – the most common type of irregular heart rhythm that can increase risk of stroke. In the UK, one million people are known to be affected by AF and an additional 422,600 people are undiagnosed. This irregular heart rhythm is responsible for approximately 20% of all strokes, which can leave survivors with disabling consequences. Treating the condition costs the NHS over £2.2 billion each year.
Making sure people with AF are given optimal treatment – usually blood-thinning medication to prevent clots (anticoagulants) – can more than halve their risk of having a stroke.
AHSNs have played a key role in this nationwide initiative. Pulse checks for over 65’s, mobile ECG devices for GP surgeries and pharmacies, and new ‘virtual clinics’ involving specialists working with GPs to advise on the best treatment for people with the condition, were amongst the varied activities undertaken as part of this life saving work.
As a result, last year over 61,000 people were diagnosed with AF for the first time and almost 80,000, including some who were previously diagnosed, were given appropriate medication.
Professor Gary Ford, Chief Executive of Oxford Academic Health Science Network and Consultant Stroke Physician said “Spotting the risk of stroke early and taking preventative measures can help to reduce risk of premature death and reduce the number of people who experience life-changing, long-term disability due to stroke. Identifying people who have AF and ensuring they are provided with the most appropriate anticoagulant (blood thinning) therapy can more than halve their risk of having a stroke.
“Since 2016 AHSNs have worked tirelessly with others across the healthcare system to reduce the burden of stroke. This recently released data illustrates the significant impact our work has made, improving lives and reducing cost to the NHS.”
What has stroke prevention in south London looked like?
During the 2018-19 financial year, the Health Innovation Network’s Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation programme achieved success in improving the detection and treatment of AF in south London through the spread and adoption of digital innovation in high-impact settings.
The team’s Mobile ECG Devices Project report, released in September 2019, describes how from January 2018 to March 2019 a total of 400 mobile ECG devices—Kardia Mobile, WatchBP and MyDiagnostick—were distributed across the 12 south London boroughs, resulting in the recording of 14,835 pulse rhythm checks and the detection of nearly 600 possible cases of AF, potentially preventing 23 strokes with estimated savings of £309,000 to health services.
AF checks in the identified high impact settings – flu vaccination clinics, community podiatry clinics and all three mental health trusts – are now in active implementation. This significant progress falls in line with the data collected since 2015, which shows that the number of strokes caused by known AF in south London has significantly reduced. The latest national stroke audit data has now been published and shows that in the two-year period from April 2017-March 2019 there were approximately 150 fewer AF-related strokes in South London than would have been expected from the previous years’ data. This is particularly impressive in the context of the increasing population age.
HIN’s AF team is continuing to support these high-impact settings and we would be delighted to hear from member organisations interested in getting involved in this life-saving work.
