While we have a great reputation for discovery in healthcare in the UK, which long predates the existence of the NHS, my recent chapter in Leading Reliable Healthcare argues that there is much more we could do to achieve spread, and that a focus on this would be an important way to achieve legacy from the abundance of entrepreneurial and creative talent that exists in this country in life sciences, digital health, clinical research and process improvements.
This blog expands on this topic further, bringing in thoughts both from the chapter and elsewhere to outline ideas on a manifesto for spread that I think we need to find a way to put in place, as a matter of some urgency.
It is important to acknowledge that there is a variety in the types of innovations; from new devices to digital tools, concepts and processes can be the most significant in changing care design. The chapter starts with a working definition:
“When we talk about “innovation” in the NHS, what do we mean? In the author’s opinion, the most useful is “an idea, service or product, new to the NHS or applied in a way that is new to the NHS, which significantly improves the quality of health and care wherever it is applied” (Taken from Innovation, Health and Wealth, Sir Ian Curruthers, Department of Health 2011).
Spend on spread
Spread has a cost, it is not a free good as clinicians and organisations need some support in adopting any new intervention or product within their practice. In innovative companies they see that communicating and supporting spread really matters and invest in spread related activities. Analysis completed by the AHSN Network indicates that there is a consistent ratio that the most admired companies seem to use.
Regardless of whether you are Apple or GE or a pharma company, the spend on spread activities including sales and marketing is typically over 2.5 times your investment in R&D, so 250-300%. In the NHS, we currently spend less than 1% of our £1.2bn R&D annual spend, on actively spreading it, and this ratio simply looks wrong. It was cited recently in Falling short: Why the NHS is still struggling to make the most of new innovations, a Nuffield Trust publication.
Within the chapter, I interview a range of people to hear their perspectives, particularly on spread and diffusion. Sir Bruce Keogh observes that “the spread can be more important than the innovation in terms of making a difference to people’s lives”. He offers that perhaps the most important single technical innovation to impact the health service is the microscope, invented by the Dutchman Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (“the father of microbiology”) in 1683. But what made a huge difference to adoption was that the president of the Royal Society, Robert Hook, wrote a beautifully illustrated book in English about it called Micrographia, understanding the significance this breakthrough could have in understanding disease. His book became “the first scientific best-seller” and “captured the public’s imagination in a radically new way; Samuel Pepys called it ‘the most ingenious book that I ever read in my life”.
Valuing innovation as much as invention
I’m currently reading James Barlow’s comprehensive assessment of “Managing Innovation in Healthcare” where he puts the distinction between invention and innovation beautifully: “an invention is merely a nascent innovation and it may be many years before it makes it to innovation status” p43. He also quotes Schon’s succinct definition: “Innovation is ‘the process of bringing inventions into use’” p25, and I believe we forget this at our peril. James is Professor of Technology and Innovation (Healthcare) at Imperial College Business School and I’d heartily recommend his new book if you’d like to get into this topic in greater depth, details are referenced at the end of this blog.
Elsewhere – in an article entitled “We’re serious about innovation – now let’s get serious about spread” – I state “spread – meaning at scale adoption of an innovation – is the way we will move from unwarranted variation in the NHS; from pockets of poor performance contrasting with beacons of excellence, often in a single geography, to improvements at scale to touch many more lives”. Within the piece I suggested if we were really serious about it we might celebrate and reward spread activities more vigorously, for example, introducing a Nobel Prize for spread rather than only congratulating discovery. Intelligent alignment is also critically important, so that different parts of the NHS and social care systems are set up and incentivised to adopt, including but not limited to financial rewards and methods of tracking data on progress. A transformation fund for hard pressed NHS institutions keen on spread would make a real difference in the current climate. It is welcome that the Office for Life Sciences has announced it will be setting one up, particularly to help parts of the NHS adopt innovations, and interesting that this is coming from a separate part of government than health, as a result of the Accelerated Access Review.
Importantly, that’s not to give the impression the NHS wouldn’t benefit hugely from additional resource as has been articulated clearly by the CEO of the NHS, Simon Stevens. In my view, this is essential, as we face the combined demands of an ageing population and increasing chronic disease burden. But were the NHS to receive an appropriately generous financial settlement, I would like to see proper funding of spread activities, so that we can get the best well-evidenced solutions – that help patients, clinicians and often make better use of resources in the longer term – to as many people, as quickly as possible.
It is interesting to see that across the channel the French government has established 14 regional tech transfer hubs with a budget of one billion euros to draw up, including investing in the strongest digital ideas, many of them in the health sphere. Eight years ago, it also introduced a system to make certain innovations available entirely free of charge to its healthcare system, as referenced by Barlow: “Since 2010, France has operated a system for conditionally covering the full cost of selected innovative devices, services or interventions which appear promising but for which there is insufficient data on the clinical benefit.” (p218)
Reaching many patients as a priority is a sentiment agreed with strongly by all of the interviewees, Tony Young emphasises the unique opportunity we have within the NHS: “The NHS is the single largest unified healthcare system in the history of the human race. This gives us some opportunities that no one else has had the chance to do— and one of them is to innovate at scale. It’s complex and divided— but that’s what gives us the opportunity to say well let’s have a go at it. If you really want to do this at scale, then we can do this in the NHS. Recently, 103 of the brightest clinicians you could ever want to meet were selected to be a part of the Clinical Entrepreneur programme and came together for their first weekend recently. Never before has there been a cohort at such a scale of clinical entrepreneurs who’ve worked together on the planet, ever”.
Skilling up for ‘scale ups’, not just ‘start ups’
Helen Bevan draws a distinction between the skills required for start-up v scale up: “What I think is one of the biggest problems that I see now, is the issue between start-up and scale-up. We have, in my mind, a system that is primarily designed for start-up— and what we keep doing is to put in charge the kind of people that love doing early-stage invention and early innovation. They’re your pioneers, your early adopters. What we keep doing is going over and over the cycle, of start-up again to attempt to spread and scale. But we’ve only got so far. We need a lot a lot of additional thinking … and need to find the people who are good at scale-up, and put them in charge of this activity, not the people who are good at start-up”. Her addition to David Albury’s work at the Innovation Unit, in creating a “checklist for scale” is incorporated as a figure in the book.
Research and data
James Barlow highlights that spread in healthcare has been under-researched to date: “situations involving collective or organisational decisions have been relatively neglected by researchers. Finally, until relatively recently, there was little research on the adoption and diffusion of innovation in the public or non-profit sectors.” P161. The exceptions to this include pioneers such as Trish Greenhalgh of Oxford and Ewan Ferlie of King’s as well as Ritan Atun at Harvard and those in the Imperial group.
Ian Dodge adds “We’re also systemically atrocious at using data systematically. For instance, looking at population outcomes of what’s happening at the end of a service line change, getting rapid feedback, iterating. Some of the initial bit of improvement science is so vital to getting stuff off the ground, but then typically we see really poor engineering discipline, factory style, around how do you actually convert this at scale”.
Clinical innovators and spread
In the chapter, some interesting examples of where spread activity is beginning to work in the English NHS are referenced, calling out the NHS Innovation Accelerator which seeks to accelerate uptake of high impact innovations and provides real time practical insights on spread to inform national strategy. Given publishing deadlines, I wrote the chapter more than a year ago, and it is both fascinating and encouraging to see how the NHS Innovation Accelerator – a programme supported by all 15 Academic Health Science Networks (AHSNs) and NHS England, coordinated by UCL Partners – has gone from strength to strength in this time in terms of tangible results of achieving scale.
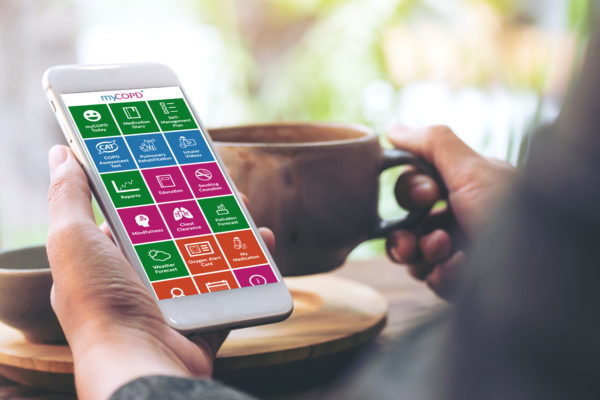
It is also striking that many of the innovations on the Accelerator have been developed by innovative NHS clinicians who spotted opportunities to improve care – making it safer and more effective. For instance, Simon Bourne, a consultant respiratory physician at Portsmouth Hospital devised myCOPD, an online platform that helps patients self-manage with dramatic results, Dharmesh Kapoor, a consultant obstetrician at Bournemouth Hospital invented Episcissor-60, scissors specifically designed to make childbirth safer, Maryanne Mariyaselvam, a doctor in training working in research in Addenbrookes, came up with the NIC a device that prevents tragic accidents with blood lines, Peter Young, a consultant anaesthetist at King’s Lynn Hospital created a ventilation tube that prevents the most serious complication of ITU care.
All the products referenced are now eligible for NHS England’s Innovation and Technology Tariff which began in April 2017 and enables NHS Trusts and CCGs in England to use these innovations either for free or to claim a charge per use. It is an important scheme and would be very valuable to see it expanded in future years.
Taking the myCOPD example, it is really interesting to see the impact of this support in terms of scale-up. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder or COPD is a progressive disease, meaning it gets steadily worse over time, and people living with it find that exacerbations increase and they are admitted to hospital more and more frequently. In fact, COPD is the second most common reason for hospital admissions in the country, causing a great deal of distress to people and families and costing the NHS over £800m in direct healthcare costs. Studies have also found that 90% of people with COPD are unable to take their medication correctly. The myCOPD on line platform has been found to correct 98% of inhaler errors without any other clinical intervention.
If you have COPD, there is a great deal you can do to help yourself avoid exacerbations, but it can be hard to do these things consistently, alone. The evidence demonstrates that those who manage to quit smoking, do regular exercises known as pulmonary rehab, have optimal inhaler technique and are able to resist the understandable urge to panic when breathless, do much better than those who do not. Simon’s support system for people with COPD has educational, self-management, symptom reporting, mindfulness and pulmonary rehabilitation aspects, all delivered online. Typical quotes from grateful patients include “Since I started using myCOPD, I have lost weight, my depression has lifted, and I see my GP just once a year (compared with twice-monthly visits previously). I have not needed hospital treatment for 18 months”, “last year, before using myCOPD, I had 12 exacerbations. This year I have had just two.”
The programme is now being used by over 55,000 people with severe COPD in England, which is roughly one-quarter of that population, with more CCGs and respiratory teams coming on board each week. I think it is fantastic that people living with this chronic condition that responds well to regular exercise and relatively simple interventions, now have a tool in their pocket that can help them better manage it, and it is very appropriate that this is NHS funded. What’s more, this expansion has been pacy and achieved in around 18months.
I discuss this further in a blog entitled “Finally, a tariff for digital innovations” – you can perhaps hear the note of impatience in the title – and state that while it is a much needed start, we need to go further faster and expand the scheme to accelerate the adoption of great tools like these that are essential for patients with long term conditions seeking to stay as well as possible. Funding six devices/tool types in its first year, only one of which is digital, the programme has started very modestly compared to the scale of investment of our counterparts in France for example.
Patient-led innovation
There have also been some great examples of patient-led innovations succeeding recently. The three London AHSNs founded Digital Health.London with MedCIty in 2016 and established an accelerator focused on spreading the best digital health solutions across the capital. On our founding cohort was Michael Seres, an incredibly entrepreneurial patient who had designed a tool to link stoma bags with smartphones via Bluetooth, to increase the dignity of the user and ensure alerts were provided when bags were reaching capacity, who is now CEO of 11 Health. The ostim-i had achieved sales in other countries but not the UK when Michael joined our programme and we were delighted that the first NHS contract has been achieved in west London. It is also available to patients to buy direct, as is the myCOPD tool. The ostim-i has been a beneficiary – as was myCOPD – of the development fund we have to support interesting UK concepts, the Small Business Research Initiative or SBRI fund – subject of my most recent blog “Why SBRI matters”.
But there are many more ideas out there, developed by patients, parents of patients and carers alongside entrepreneurs and clinicians and we need to radically increase the capacity to give them the support they need. I am encouraged that the Office for Life Sciences, part of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, is investing in creating Innovation Exchanges, hosted by AHSNs to increase the support to local innovators, with funding due early in this new year and committed to for three years. The need to provide stronger support to UK companies and ideas is felt all the more intensely given Brexit.
I conclude the chapter “While there is plenty to do, it feels as though there is reason for optimism that the entrepreneurial zeal at the heart of our health system will continue to burn brightly and that more recent learning and focus on collaboration and scale will help us to ensure that the best ideas in health and care are disseminated more widely across the NHS.”
A system for spread
A year on, I remain optimistic; we’ve had commitments made as a result of the Accelerated Access Review, it has been announced that AHSNs will be relicensed to operate as the innovation arm of the NHS and we have strong spread and progress particularly through our major collaborations – the NHS Innovation Accelerator and in the capital through Digital Health.London, NHS England has made an important start in a tariff for innovation.
However, my view is that we need many more including our regulators, politicians, NHS staff, patients and their representatives to join this movement if we are to achieve the change we need to take place, and be much bolder about our commitment to spread. To see all NHS organisations join the best in moving beyond “not invented here” to truly rewarding adoption and diffusion activities and acknowledging that change needs support to be durable, and happens at the speed of trust.
We need our inspection regimes and regulators to really get this and understand the behavioural insights we now know about achieving sustainable diffusion and change, and leaders supporting staff through these changes not resorting to an over simplistic and non-evidence based paradigm that telling will result in adherence.
If the spread movement was to achieve this level of support across the NHS, we would then be able to enact all aspects of the manifesto for spread and with support for these principles, and the action required, including investment in supporting NHS organisations scale up innovation, and I believe it could be possible to make significant change happen quickly.
Acknowledgments
I am very grateful to all those people I’ve discussed this topic with and particularly Suzie Bailey, Richard Barker, Helen Bevan, Ian Dodge, Sir Bruce Keogh, Becky Malby and Tony Young for the generous support they have lent to the chapter and to Stephanie Kovala for all her assistance in compiling it.
Suzie Bailey is Director of Leadership and Quality Improvement at NHS Improvement, Richard Barker is Chair of Health Innovation Network and CEO New Medicine Partners, Helen Bevan is Chief Transformation Officer, Horizons Group, NHS England, Ian Dodge is National Director, Strategy and Innovation, NHS England, Sir Bruce Keogh was Medical Director, NHS England to Dec 17, Becky Malby is Professor Health Systems Innovation at London South Bank University and Tony Young is National Clinical Lead for Innovation at NHS England as well as Consultant Urological Surgeon within the NHS. Stephanie Kovala was my Business Manager and is now Project Manager within the Strategy Team at NHS England.
Author: Tara Donnelly is CEO of Health Innovation Network, the academic health science network for south London. Health Innovation Network exists to speed up the best in health and care, together with its members in south London, and is part of the AHSN Network and Digital Health.London.
Follow Tara on Twitter at @tara_donnelly1
References:
AHSN Network: ahsnnetwork.com
Al Knawy, B. Editor, Leading Reliable Healthcare, Chapter 12 – Health System Innovation and Reform, Productivity Press CRC, Dec 2017
Barlow, J. Managing Innovation In Healthcare, New Jersey: World Scientific, 2017
Castle-Clarke S, Edwards N, Buckingham H. Falling short: Why the NHS is still struggling to make the most of new innovations. Nuffield Trust Briefing Dec 2017
Curruthers, I and Department of Health, NHS Improvement & Efficiency Directorate, Innovation and Service Improvement, 2011. Innovation, Health and Wealth, Accelerating Adoption and Diffusion in the NHS
Digital Health.London: digitalhealth.london
Donnelly, T. Sept 2016. We’re serious about innovation— now let’s get serious about spread. Health Service Journal
Donnelly, T. Nov 2017. Finally, a tariff for digital innovations. Healthcare Digital
Donnelly, T. Dec 2017. Why SBRI matters
Health Innovation Network: healthinnovationnetwork.com